[…] the mechanics of how FRP code is executed. In most FRP systems, this all happens at application runtime. There are two stages:
Stage 1: Initialization—Typically during program startup, FRP code statements are converted into a Directed Graph in memory.
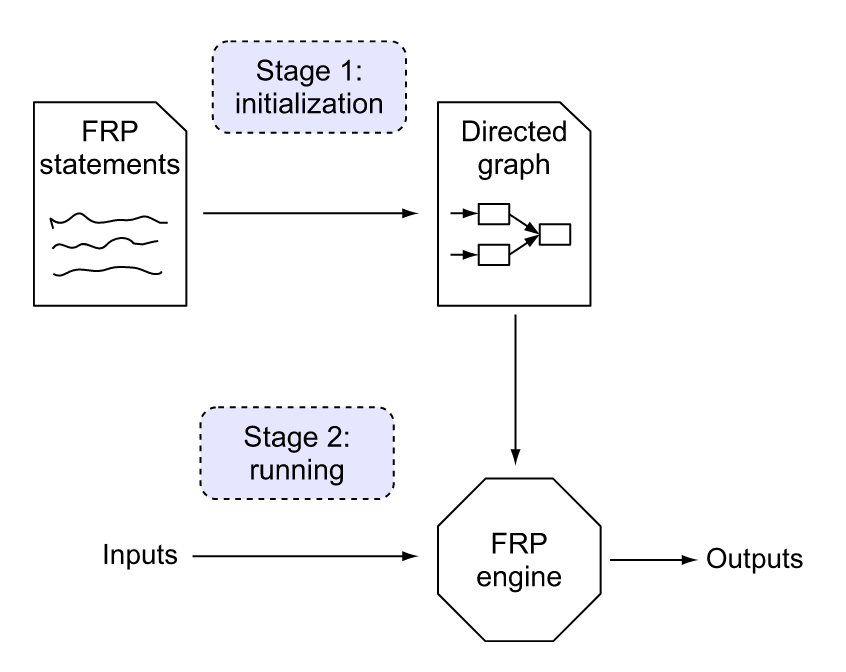
The stages of execution of an FRP program (Blackheath/Jones 2016, p. 13.)
Stage 2: Running—For the rest of the program execution you feed in values and turn the crank handle, and the FRP engine produces output.
~
BLACKHEATH, Stephen and JONES, Anthony, 2016. Functional Reactive Programming. Manning Publications. ISBN 978-1-63343-010-5, p. 13.
Functional Reactive Programming teaches the concepts and applications of FRP. It offers a careful walk-through of core FRP operations and introduces the concepts and techniques you’ll need to use FRP in any language.
About the Technology. Today’s software is shifting to more asynchronous, event-based solutions. For decades, the Observer Pattern has been the go-to event infrastructure, but it is known to be bug-prone. Functional reactive programming (FRP) replaces Observer, radically improving the quality of event-based code.
About the Book. Functional Reactive Programming teaches you how FRP works and how to use it. You’ll begin by gaining an understanding of what FRP is and why it’s so powerful. Then, you’ll work through greenfield and legacy code as you learn to apply FRP to practical use cases. You’ll find examples in this book from many application domains using both Java and JavaScript. When you’re finished, you’ll be able to use the FRP approach in the systems you build and spend less time fixing problems.
What’s Inside. Think differently about data and eventsFRP techniques for Java and JavaScriptEliminate Observer one listener at a timeExplore Sodium, RxJS, and Kefir.js FRP systemsAbout the ReaderReaders need intermediate Java or JavaScript skills. No experience with functional programming or FRP required.About the AuthorsStephen Blackheath and Anthony Jones are experienced software developers and the creators of the Sodium FRP library for multiple languages.
A directed graph is a Data Structure containing a vertex set <i>V</i> and an <i>arc</i> set <i>A</i>, where each arc (or <i>edge</i>, or <i>link</i>) is an ordered pair of vertices (or <i>nodes</i>, or <i>sommets</i>). The arcs may be thought of as arrows, each one starting at one vertex and pointing at precisely one other.